How to use Memcached in a UNIX socket
Memcached can run in a UNIX socket, which provides better performance than a TCP connection.
Note: If Memcached fails to start, it is usually due to permission and user problems. Please use root privilege to execute the following instructions, and verify that the socket path is writable to the designated user.
For Centos7.X
- Stop Memcached
systemctl stop memcached
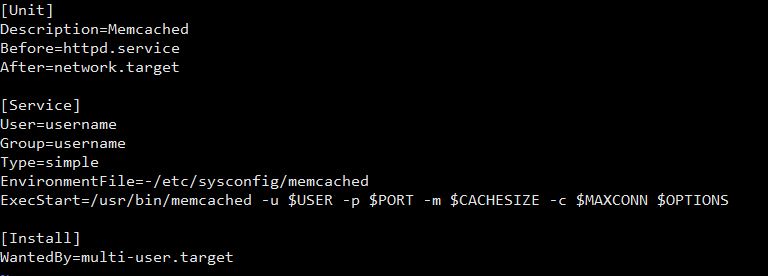
- Copy the service file
cp /usr/lib/systemd/system/memcached.service /etc/systemd/system/memcached.service
- Edit
/etc/sysconfig/memcached, changing the path to your desired location, and the username to the same one used in Step 3:OPTIONS="" USER="memcached"
becomes
OPTIONS="-s /path/to/memcached.sock -a 0770" USER="username"
- Start Memcached again:
systemctl start memcached
- Verify it started successfully:
systemctl status memcached
- Check if everything is working well:
nc -U /path/to/memcached.sock stats
- If there is still a permission issue, please check selinux status:
getenforce
- Disable selinux if status shows
Enforcing:setenforce 0
(reboot will re-enable selinux)
- To permanently disable selinux, edit
/etc/selinux/config, changeenforcingtopermissiveordisabledand then reboot.
for Centos6.X
- Stop Memcached
systemctl stop memcached
- Edit
/etc/sysconfig/memcachedand changeOPTIONS="" USER=""
to
OPTIONS="-s /path/to/memcached.sock -a 0770" USER="username"
where USER is the same user that runs PHP.
- Start Memcached
service memcached start
- Check if everything is working well:
nc -U /path/to/memcached.sock stats
- If there is still a permission issue, please check selinux status:
getenforce
- Disable selinux if status shows
Enforcing:setenforce 0
(reboot will re-enable selinux)
- To permanently disable selinux, edit
/etc/selinux/config, changeenforcingtopermissiveordisabledand then reboot.
For Ubuntu 17.10, Ubuntu 16.04, Debian 8 and Debian 9
- Stop Memcached
systemctl stop memcached
- Edit
/etc/memcached.conf, comment out host and port, add socket path and permission-s /path/to/memcached.sock -a 0770
and change
-u memcacheto-u usernamewhereusernameis the same user that runs PHP. - Start Memcached again
systemctl start memcached
- Check if everything is working well:
nc -U /path/to/memcached.sock stats
for Ubuntu 14.04 and Debian 7
- Stop Memcached
service memcached stop
- Edit
/etc/memcached.conf, comment out host and port, add socket path and permission-s /path/to/memcached.sock -a 0770
and change
-u memcacheto-u usernamewhereusernameis the same user that runs PHP. - Start Memcached again
service memcached start
- Check if everything is working well:
nc -U /path/to/memcached.sock stats